Laboratory test results with Spectral Blue MWHI blue light
 IMAGE: Spectral Blue device being tested against SARS-CoV-2 at University of Helsinki, 2022
IMAGE: Spectral Blue device being tested against SARS-CoV-2 at University of Helsinki, 2022
On this page you can find public laboratory test results with Spectral Blue Multi-Wavelength, High Intensity (MWHI) technology. The tests have been done by independent 3rd party laboratories or researchers.
The tests typically show the efficacy of one disinfection cycle (1-8 hours) against a high starting concentration of microbes. In continuous use the system will automatically perform a large number of such cycles over time. Continuous use prevents microbial growth and keeps your premises at a high hygienic level all the time.
- Listeria monocytogenes - Atria Finland Ltd, QA laboratory (2024)
- Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus under organic load - University Clinic of Bonn (2023)
- SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus - University of Helsinki (2022)
- Escherichia coli - MetropoliLab (2020)
- Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA/MRSA) - MetropoliLab (2019)
- Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enterica Typhimurium and Candida albicans - Master's thesis, University of Eastern Finland (2019)
- Escherichia coli - Turku University of Applied Sciences (2018)
Updated October 2024.
Listeria monocytogenes - Atria Finland Ltd, QA laboratory
In Summer 2024, the food QA laboratory of Atria Finland Ltd tested the performance of Spectral Blue SALO XL device against Listeria m. in a biosafety cabinet.
Samples were analyzed according to ISO 11290-2:2017 to determine the number of viable Listeria m. colonies after treatment with blue light.
The results demonstrate that Spectral Blue is highly effective against the most challenging food-borne microbes and can be utilized in biosafety cabinets to prevent cross-contamination and reduce the risk of infection to staff.
Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus under organic load - University Clinic of Bonn 2023
In Summer 2023, LED Tailor commissioned University Clinic of Bonn (Institut für Hygiene und Öffentliche Gesundheit) to perform an efficacy test on Spectral Blue disinfection technology against Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus under organic load.
The investigation was designed to follow applicable EN standards and to simulate real-life conditions such as in healthcare or ambulance use, where organic load can be present on surfaces.
The results of the investigation demonstrate that Spectral Blue MWHI technology has a germ-reducing effect on all the tested micro-organisms.
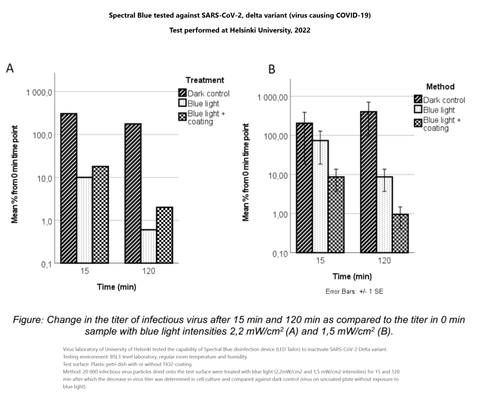
SARS-CoV-2 (Coronavirus) - University of Helsinki, Virus laboratory (2022)
Virus laboratory of University of Helsinki tested the capability of Spectral Blue disinfection device (LED Tailor) to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that has cause the COVID-19 pandemic.
Testing environment: BSL3-level laboratory, regular room temperature and humidity.
Test surface: Plastic petri dish with or without TiO2-coating.
Method: 20 000 infectious virus particles dried onto the test surface were treated with blue light (2,2mW/cm2 and 1,5 mW/cm2 intensities) for 15 and 120 min after which the decrease in virus titer was determined in cell culture and compared against dark control (virus on uncoated plate without exposure to blue light).
Conclusion: In these testing conditions, treatment with Spectral Blue leads to significant decrease in the amount of infectious SARS-CoV-2 on dry plastic surface.
Escherichia coli - MetropoliLab (2020)
In summer 2020, laboratory tests were conducted at the FINAS accredited MetropoliLab to determine the efficiency of LED Tailor's Spectral Blue device in inactivation of E.coli (ATCC 25922).
The bacteria were spread out on the bottom of plastic petri dishes and irradiated with low intensity blue light (0,7 mW/cm2) under regular office conditions.
Each test result contains three parallel samples from each point of analysis. Error bars show SD (standard deviation).
Conclusion: 4-hour irradiation with Spectral Blue resulted in reduction of over 95%. When used together with photocatalytic TiO2 coating, a reduction of 99% was achieved already after 30 minutes.
Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA/MRSA) - MetropoliLab (2019)
In spring 2019, laboratory tests were conducted at the FINAS accredited MetropoliLab to determine the efficiency of LED Tailor’s Spectral Blue disinfection device in inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) with the photocatalytic coating.
The bacteria were plated on a regular melamine tabletop and irradiated at low intensity (blue light 0,7 mW/cm²). The results were confirmed by conducting three separate tests, with each test utilizing three parallel samples from each point of analysis.
Conclusion: 8-hour irradiation with Spectral Blue resulted in reduction of over 90%. When used together with photocatalytic TiO2 coating, the result was over 99.9% reduction.
Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enterica Typhimurium and Candida albicans on top of food products - Master's thesis, University of Eastern Finland (2019)
K. Ojala: Antimicrobial Effect of Blue Light on the Spoilage Microbes and on the Microbiological Safety of Food (2019)
University of Eastern Finland, Faculty of Health Sciences
Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition
Link: https://erepo.uef.fi/handle/123456789/21815?locale-attribute=en
Aim of this thesis was to evaluate if the microbiological safety of the ready-to-eat products can be improved with blue light without additional decontamination treatments. Three microbes were exposed to either blue light (405 nm) or UV-light (254 nm) both in microbial suspension and on top of a food product at +4 °C for 24 h. Control samples were held in the dark with otherwise identical conditions. Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 7644 were inoculated on top of smoked salmon, Salmonella enterica Typhimurium ATCC 13311 on top of cooked chicken and Candida albicans ATCC 90029 on top of raspberry marmalade.
Conclusions: Based on these results blue light could be used to improve the microbial safety of the food on certain products, but the properties of the product greatly affect the efficacy of the light. More research needs to be done on the efficacy of the blue light with different food products and microbes.
Escherichia coli - Turku University of Applied Sciences (2018)
In spring 2018, laboratory tests were conducted at the Turku University of Applied Sciences to determine the efficiency of LED Tailor’s Spectral Blue device in the inactivation of Escherichia coli. The bacteria were plated on agar and irradiated at a low intensity (0,7mW/cm2). The results were confirmed by conducting three separate tests, with each test utilizing three parallel samples from each point of analysis.
Conclusion: 6-hour irradiation with Spectral Blue resulted in reduction of over 99.9%.